Hepatis B
A serious liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus that’s easily preventable by a vaccine.
Spreads by sexual contact
Preventable by vaccine
Treatable by a medical professional
Requires a medical diagnosis
Lab tests or imaging always required
This disease is most commonly spread by exposure to infected bodily fluids.
Symptoms are variable and include yellowing of the eyes, abdominal pain and dark urine. Some people, particularly children, don’t experience any symptoms. In chronic cases, liver failure, cancer or scarring can occur.
The condition often clears up on its own. Chronic cases require medication and possibly a liver transplant.
How it spreads
By blood products (unclean needles or unscreened blood).
By mother to baby by pregnancy, labor, or nursing.
By having unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
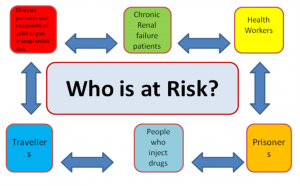
Recommendation
- Hepatitis B vaccine is the main stay of hepatitis b prevention
- It is recommended that all infants receive the hepatitis b as soon as possible after birth, preferably within 24 hours after birth and then followed by two or three dose to complete the primary series.
- All children and adolescent younger that 18 years old and not previously vaccinated should receive the vaccine.
- Travelers should be offered vaccine before leaving for endemic areas
- People who frequently require blood or blood product, dialysis patients, recipients of solid organ transplantations (NB: after laboratory screen with Hepatitis B SAb value < 10 antibodies)
- Health-care workers and others who may be exposed to blood and blood products through their work (NB: after laboratory screen with Hepatitis B SAb value < 10 antibodies)
Challenges in health settings (Dialysis sectors)
Lack of Hepatitis B SAb value evidence when a health worked is hired
No check-up or/and follow ups on health workers. Doctors issue scripts of Engerix B to patients;
- Some patients do not buy Engerix B/Hbv vaccination at all
- Some patients verbalize that they are vaccinated at local pharmacy – no proof
- Some misplace the scripts
- Some only submit first dose, skip the second/third dose and submit the last one
- Some medical aids do not cover the vaccination at all, which then becomes a burden to the patient to buy
- Some patient are not able to purchase due to working and dialysis schedule
- Some will go to an extend of skipping dialysis session due to failing to provide evidence
- Lack of knowledge about Hepatitis B and the vaccination
- At the end on of the day, the Transplant program to those who are listed becomes impossible due to lack anti-bodies.
- which is a major challenge to the patients as they are cancelled just before the commencement of Transplant procedure and some are rejected immediately.
More Articles
-
Vaccination
Understanding the difference between vaccines, vaccinations, and immunizations can be tricky
